This is an optional module that adds Python support in Chrono.
Features
The PYTHON module allows users to use Chrono modeling, simulation, and visualization capabilities using Python.
This module consists of two build targets:
- The Python modules for PyChrono.
Python wrappers are generated for the following Chrono modules (if they are enabled during CMake configuration):- pychrono, which wraps most Chrono classes, equivalent to the chrono namespace
- pychrono.fea, which wraps FEA classes, equivalent to the chrono::fea namespace.
- pychrono.fsi, which wraps FSI classes, equivalent to the chrono::fsi namespace (not available on the Mac Apple Silicon).
- pychrono.vehicle, which wraps the Chrono::Vehicle classes and ground vehicle models in the chrono::vehicle namespace.
- pychrono.robot, which wraps the various models in the Chrono robotics models library.
- pychrono.ros, which wraps the Chrono::ROS classes.
- pychrono.sensor, which wraps the Chrono::Sensor classes (not available on the Mac Apple Silicon).
- pychrono.postprocess, which wraps the Chrono::Postprocess module.
- pychrono.irrlicht, which wraps the Chrono::Irrlicht module for run-time visualization.
- pychrono.vsg3d, which wraps the Chrono::VSG module for run-time visualization, equivalent to the chrono::vsg3d namespace (not available in conda version yet).
- pychrono.pardisomkl, which wraps the Chrono::PardisoMKL module (not available on the Mac Apple Silicon).
- pychrono.cascade, which wraps the Chrono::Cascade module.
- A PYPARSER module, which is a C++ module for parsing / executing / interpreting Python instructions from C++ programs.
Requirements
- To run applications based on this module:
- you must have Python3 installed. On the Mac load the actual Python distribution from https://www.python.org and install it. Set the appropriate environment variable. Don't use the python installed by homebrew.
- to use the pychrono.cascade module you must also build and install the pythonocc-core package. For consistency with OpenCASCADE 7.9.2 (required to build Chrono::Cascade), make sure to use pythonocc-core version 7.9.0.
- To build this module:
- On Windows, use a SWIGWIN distribution which includes a pre-built executable. SWIG versions 4.0.2, 4.1.0, and 4.2.1 have been tested.
- On Linux, many distributions include packages of SWIG. Consult your package management application.
- On MacOS, don't install SWIG with homebrew. You would get SWIG 4.3.1 which generates source files with syntax bugs. Build SWIG 4.1.1 or 4.2.1 from sources.
Building instructions
- Install SWIG on your system. Version 4.0.0 or newer is required. (on Windows, just unzip where you want).
- Repeat the instructions for the full installation, but when you see the CMake window, you must add the following steps:
- Set
CH_ENABLE_MODULE_PYTHONas 'on', then press 'Configure' (to refresh the variable list) - The Python package should be detected by CMake automatically. If prompted, set the
CH_PYTHONDIRvariable to the directory where you have your copy of Python. For example, it could beC:/Python33 - If prompted, set the CMake
SWIG_EXECUTABLEvariable to specify the SWIG executable. On Linux, this should be detected automatically. On Windows, depending on how SWIG was installed, you may need to set this manually. - Press 'Configure' again, then 'Generate', and proceed as usual in the installation instructions.
If you have multiple Python installations on the same machine, you may need to explicitly specify which one to use in the call to CMake. For example, under Linux (Mac is similar to Linux):
% ccmake -DPYTHON_EXECUTABLE:FILEPATH=/usr/local/python/3.6.0/bin/python3 -DPYTHON_LIBRARY=/usr/local/python/3.6.0/lib/libpython3.so -DPYTHON_INCLUDE_DIR=/usr/local/python/3.6.0/include ../../chrono On the Mac: % ccmake -DPYTHON_EXECUTABLE:FILEPATH=$(which python3) ../../chrono
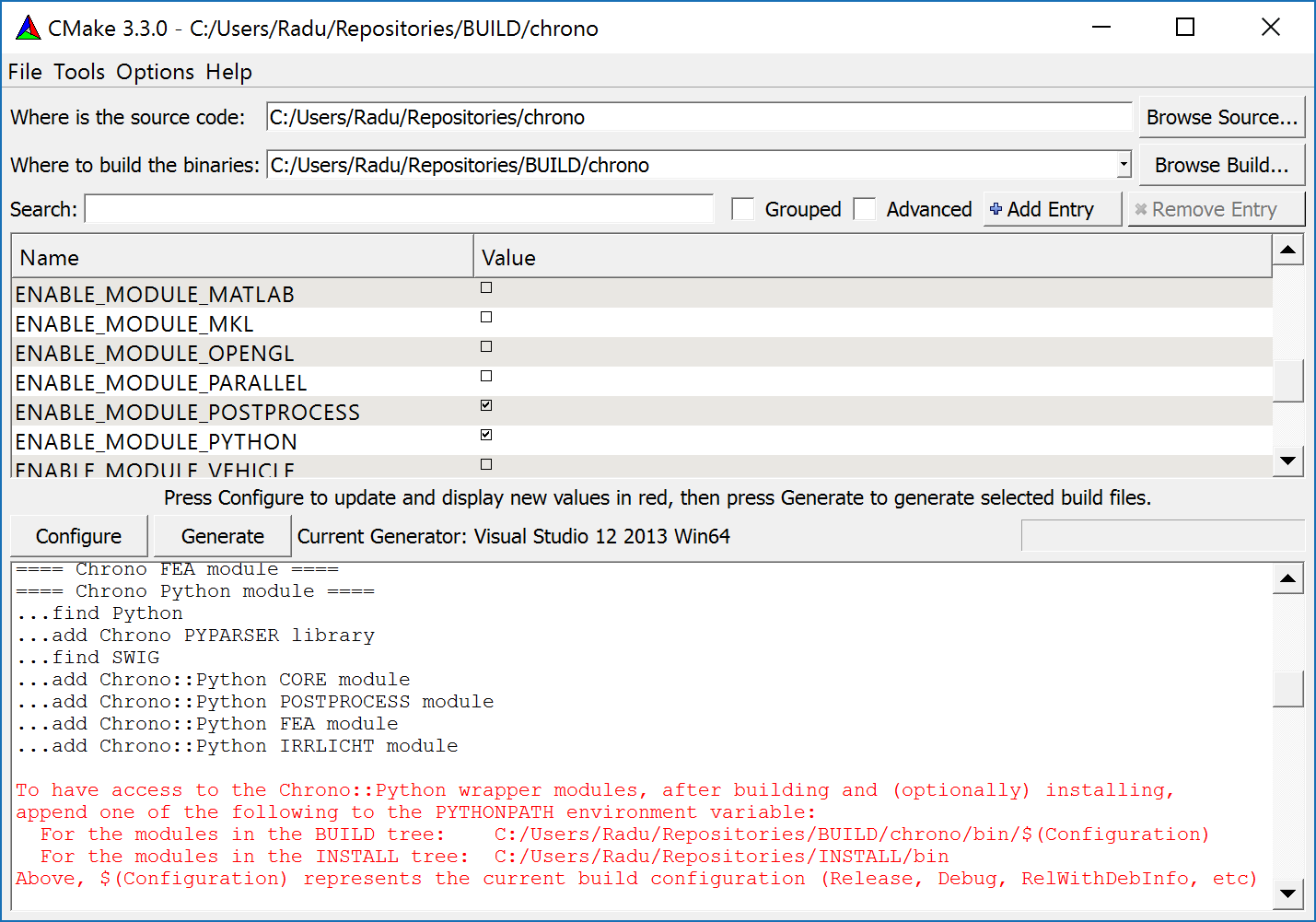
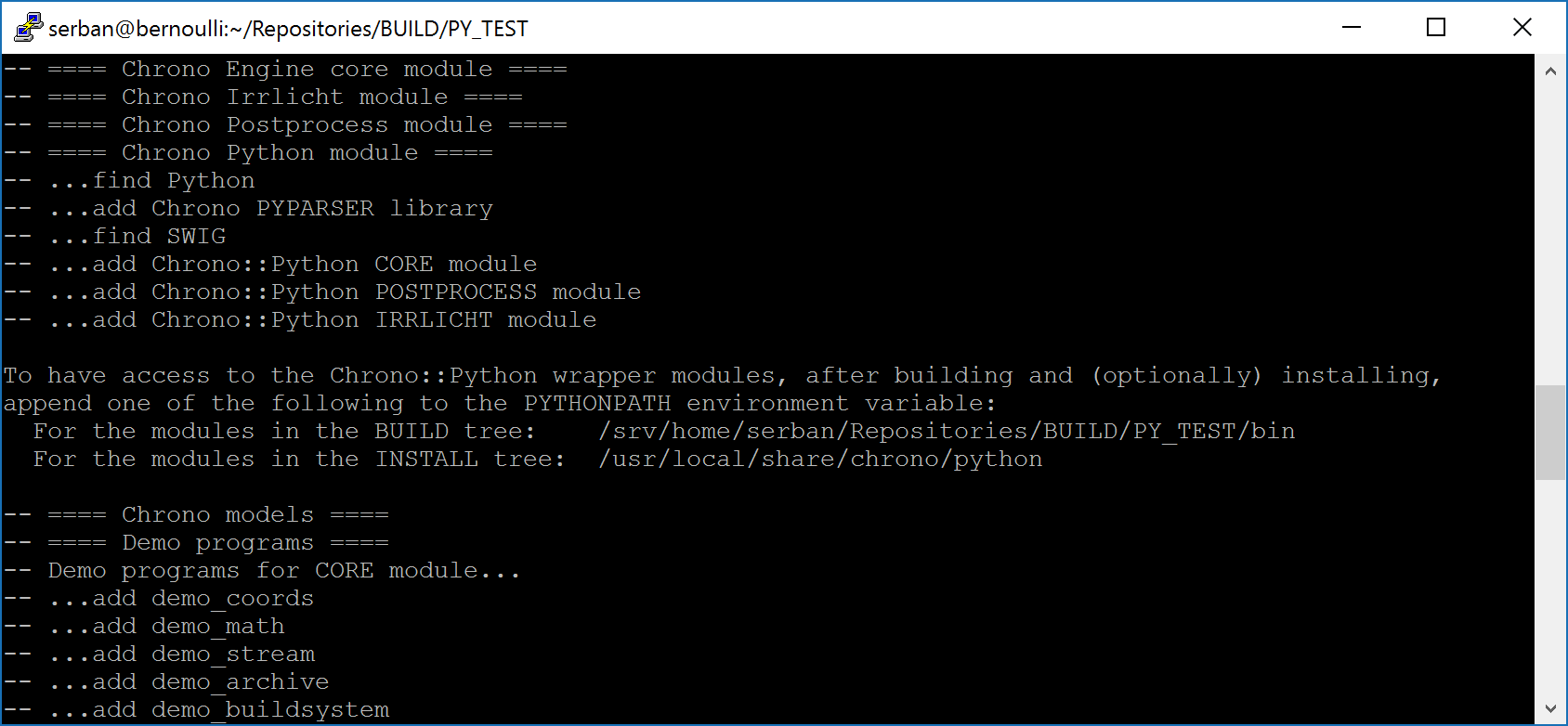
After successful compilation, the PyChrono modules can be used either from the BUILD tree or, after installation, from the INSTALL tree. In order for the generated Python modules to be accessible, you must set/append to the PYTHONPATH environment variable. During configuration, the Chrono CMake script will output the proper paths to be used in setting the PYTHONPATH environment variables; for example:
- Windows:
- Linux:
Setting/changing environment variables is platform-specific.
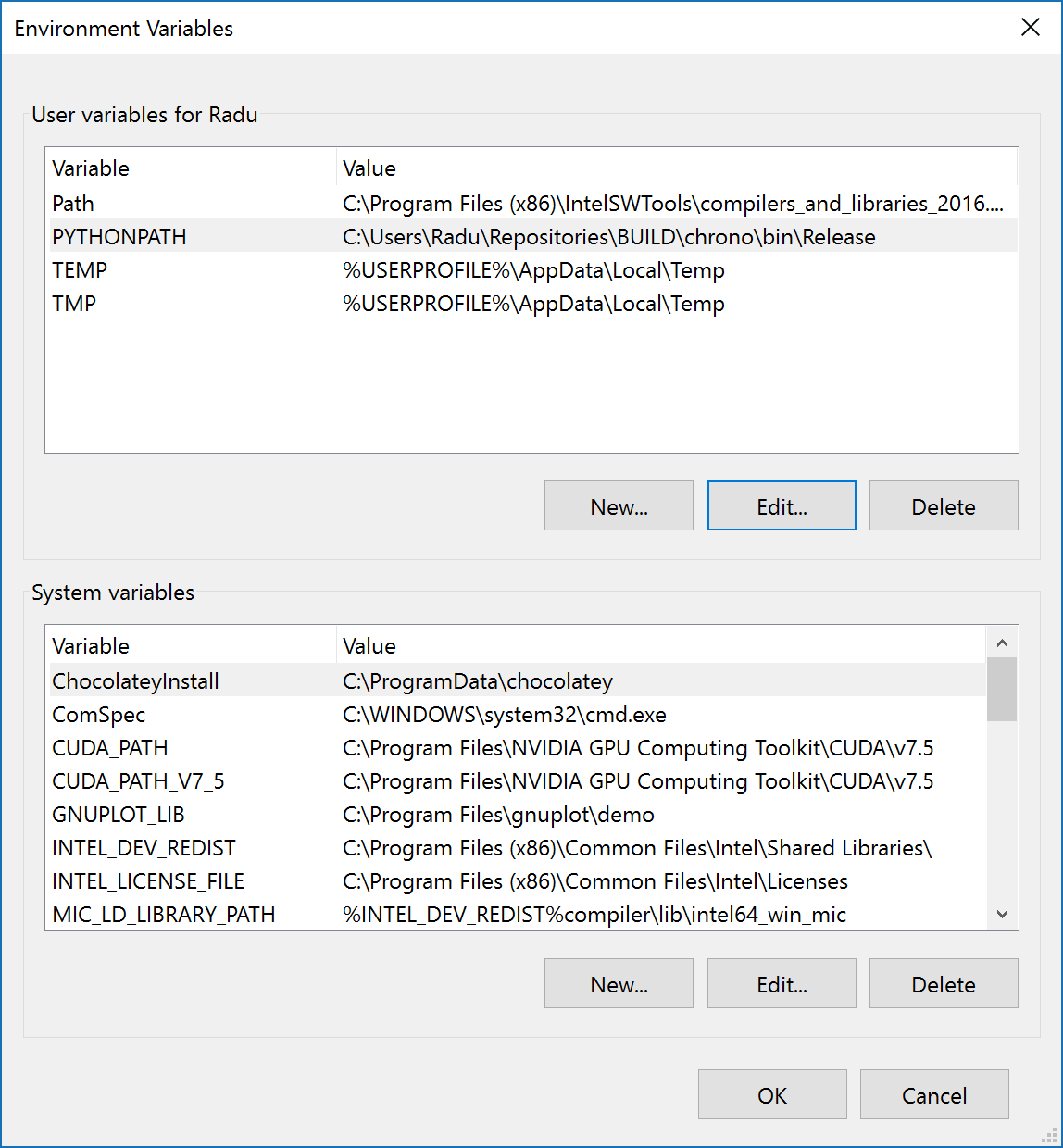
- On Windows, you can (globally) set environment variables in 'Control Panel -> System -> Advanced system settings':
- On Linux, using bash shell:
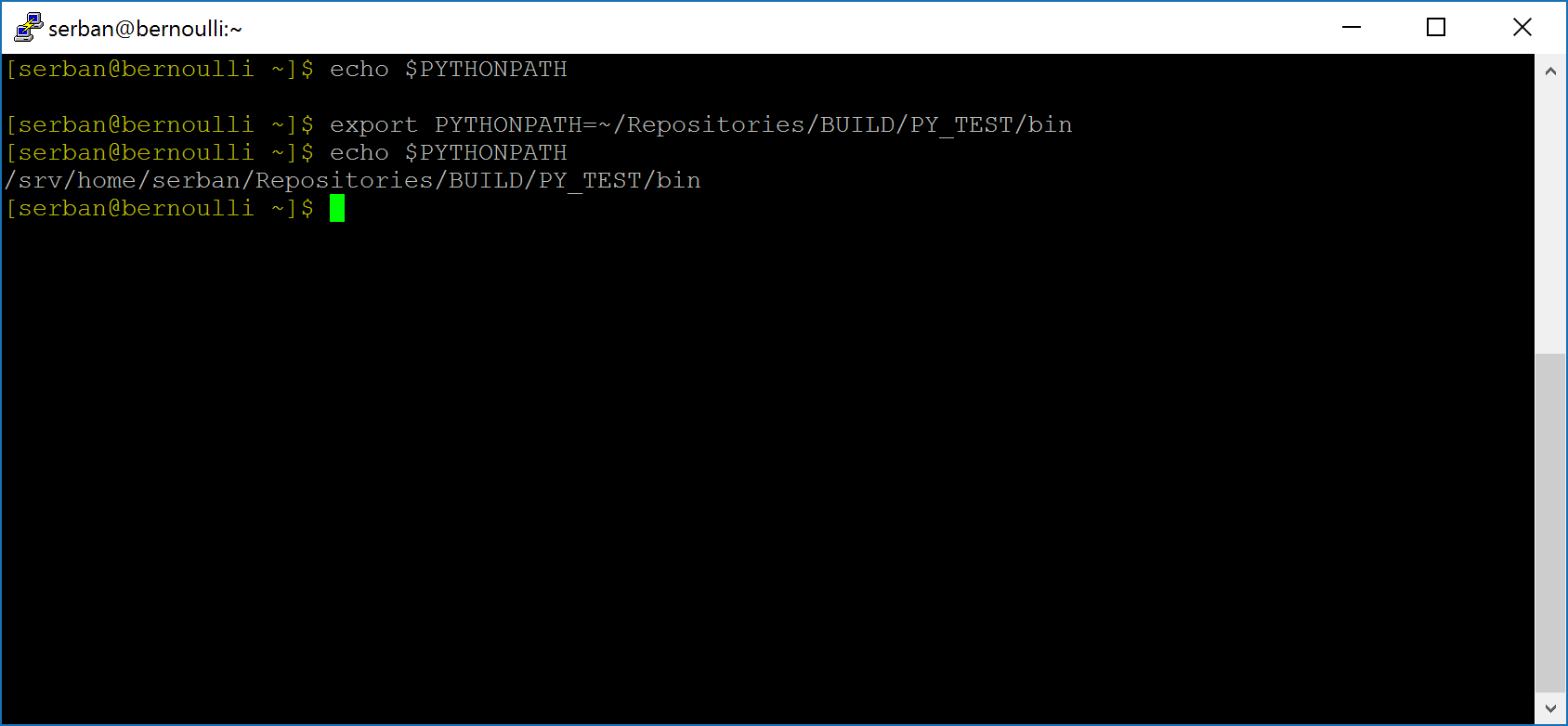
To permanently setPYTHONPATH, you can add the above to your .bashrc file (or the appropriate initialization file for your shell).
Usage
At runtime all systems need a few Python modules: numpy and six. Run this command:
pip3 list
You should see something like this:
Package Version
-------— ----—
numpy 1.22.3
pip 22.0.4
setuptools 58.1.0
six 1.16.0
You can install the missing modules with:
pip3 install numpy six
For more details on how to use the resulting modules, look here:
- C++ functions (as Python parser)
- Look at the API section of this module for documentation about C++ functions.
- Look at the C++ source of demos to learn how to use the C++ functions of this module.
- Python functions (as PyChrono )
Notes
The build process of the Python modules, as generated by CMake, consists of these automatic steps:
- SWIG preprocesses C++ source code files in order to generate a .cxx wrapper file that contains the code for accessing C++ functions through the API, and some .py files,
- the C++ compiler compiles the .cxx file and generates one or more library files,
- the SWIG-generated files (*.py) and resulting library files (*.pyd on Windows and *.so on Linux/Mac) are collected in a single location in the BUILD tree, so that they can be used directly from there. Similarly, after installation, all Chrono::Python modules are copied in a single location in the INSTALL tree. See the comments above about these exact locations for your particular configuration and about setting the
PYTHONPATHenvironment variable.
- Comment out the line: //#define Py_DEBUG
Modify
#if defined(_DEBUG)#pragma comment(lib,"python33_d.lib")to
#if defined(_DEBUG)#pragma comment(lib,"python33.lib")- Press 'Advanced' in CMake, set the PYTHON_DEBUG_LIBRARY to the same lib that you have in PYTHON_LIBRARY, and press 'Generate' so that your project will link 'python33.lib' instead than 'python33_d.lib'.
