Tutorial that teaches how to use the POSTPROCESS module to create animations with POVray.
When the simulation is run, a set of .pov and .ini files are saved on disk, so that one can use POVray later to do high-quality rendering of simulations.
Note: the same assets can be used to render animations in real-time in the interactive 3D view of Irrlicht, as explained in demo_IRR_assets.cpp
Example 1
Create a chrono::ChBody, and attach some 'assets' that define 3D shapes. These shapes can be shown by Irrlicht, OpenGL, or POV postprocessing. Note: these assets are independent from collision shapes.
auto floor = chrono_types::make_shared<ChBody>();
floor->SetFixed(true);
auto floor_mat = chrono_types::make_shared<ChContactMaterialNSC>();
auto floor_shape = chrono_types::make_shared<ChCollisionShapeBox>(floor_mat, 20, 1, 20);
floor->AddCollisionShape(floor_shape, ChFrame<>(
ChVector3d(0, -1, 0), QUNIT));
floor->EnableCollision(true);
auto boxfloor = chrono_types::make_shared<ChVisualShapeBox>(20, 1, 20);
boxfloor->SetColor(ChColor(0.3f, 0.3f, 0.6f));
floor->AddVisualShape(boxfloor, ChFrame<>(
ChVector3d(0, -1, 0)));
Example 2
Textures, colors, asset levels with transformations. This section shows how to add more advanced types of assets.
auto body = chrono_types::make_shared<ChBody>();
body->SetFixed(true);
auto sphere = chrono_types::make_shared<ChVisualShapeSphere>(0.5);
body->AddVisualShape(sphere, ChFrame<>(
ChVector3d(-1, 0, 0)));
auto mbox = chrono_types::make_shared<ChVisualShapeBox>(0.4, 1.0, 0.2);
body->AddVisualShape(mbox, ChFrame<>(
ChVector3d(1, 0, 0)));
auto cyl = chrono_types::make_shared<ChVisualShapeCylinder>(0.3, 0.7);
body->AddVisualShape(chrono_types::make_shared<ChVisualShapeSphere>(0.03),
body->AddVisualShape(chrono_types::make_shared<ChVisualShapeSphere>(0.03),
auto objmesh = chrono_types::make_shared<ChVisualShapeModelFile>();
body->AddVisualShape(objmesh, ChFrame<>(
ChVector3d(0, 0, 2)));
for (int j = 0; j < 20; j++) {
auto smallbox = chrono_types::make_shared<ChVisualShapeBox>(0.2, 0.2, 0.02);
smallbox->SetColor(ChColor(j * 0.05f, 1 - j * 0.05f, 0.0f));
body->AddVisualShape(smallbox, ChFrame<>(pos, rot));
}
auto camera = chrono_types::make_shared<ChCamera>();
camera->SetAngle(50);
body->AddCamera(camera);
Example 3
Create a chrono::ChParticleCloud cluster, and attach 'assets' that define a single "sample" 3D shape. This will be shown N times in POV or Irrlicht.
auto particles = chrono_types::make_shared<ChParticleCloud>();
auto particle_mat = chrono_types::make_shared<ChContactMaterialNSC>();
auto particle_shape = chrono_types::make_shared<ChCollisionShapeSphere>(particle_mat, 0.05);
particles->AddCollisionShape(particle_shape);
particles->EnableCollision(true);
for (int np = 0; np < 100; ++np)
particles->AddParticle(ChCoordsys<>(
ChVector3d(ChRandom::Get() - 2, 1, ChRandom::Get() - 0.5)));
auto sphereparticle = chrono_types::make_shared<ChVisualShapeSphere>(0.05);
particles->AddVisualShape(sphereparticle);
The POV exporter
The following part is very important because this is what makes this demo different from the demo_IRR_assets, that used Irrlicht. We need to create a postprocessor of type chrono::postprocess::ChPovRay and tell him that we are going to export our visualization assets:
ChPovRay pov_exporter = ChPovRay(&sys);
pov_exporter.SetBasePath(out_dir);
pov_exporter.SetLight(
ChVector3d(-3, 4, 2), ChColor(0.15f, 0.15f, 0.12f),
false);
pov_exporter.SetCustomPOVcommandsScript(
" \
light_source { \
<2, 10, -3> \
color rgb<1.2,1.2,1.2> \
area_light <4, 0, 0>, <0, 0, 4>, 8, 8 \
adaptive 1 \
jitter\
} \
object{ Grid(1,0.02, rgb<0.7,0.8,0.8>, rgbt<1,1,1,1>) rotate <0, 0, 90> } \
");
The simulation loop
Now you have to write the usual while() loop to perform the simulation. Note that before running the loop you need to use pov_exporter.ExportScript(); , and for each timestep you must use pov_exporter.ExportData(); actually this is the instruction that creates the many .dat and .pov files in the output directory.
pov_exporter.ExportScript();
std::cout <<
"time= " << sys.
GetChTime() << std::endl;
pov_exporter.ExportData();
}
Executing and rendering with POVray
Once you created your program, compile it, then:
- execute the
demo_POST_povray1.exe
- on the console you will see a time counter showing that the system is load and it is being simulated
- when the program ends, you must open POVray and open the
rendering_frames.pov.ini file, using the Open menu or button, or drag&drop (you can find this .ini file and other POVray as they are saved in the same directory of the executable)
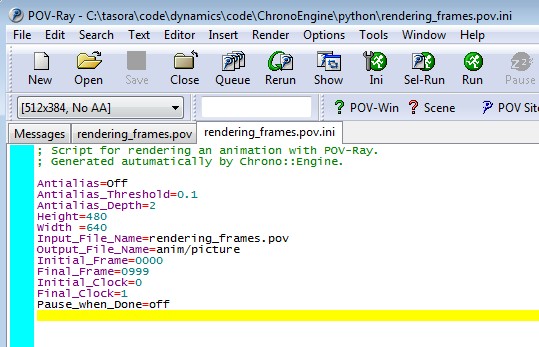
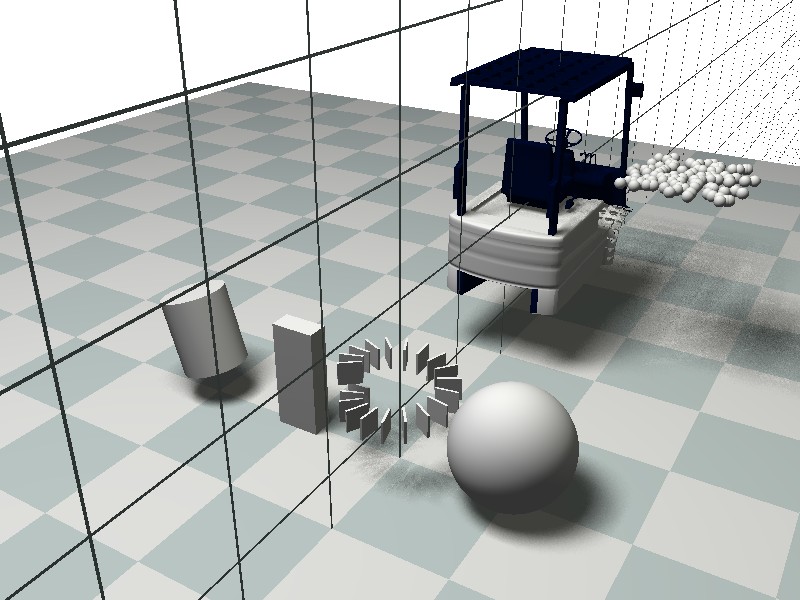
- press the Run button in POVray to execute the .ini file , and you should see that POVray generates lot of frames, being saved in the directory
anim.
Optional encoding into an AVI or MPEG animation
If you want to generate a .mpeg or .avi animation from the rendered .bmp images, we suggest to use the VirtualDub tool:
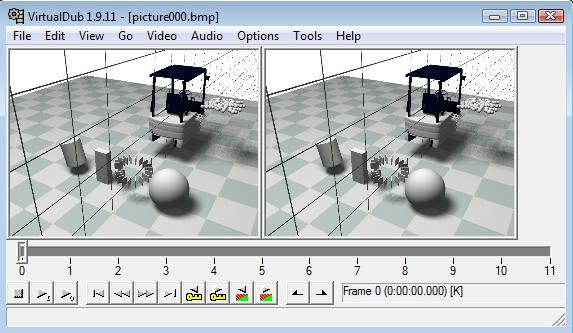
- drag&drop the first .jpg frame in its interface; it will automatically load all other frames in the timeline
- use menu Video/Compression... to setup the proper video codec (suggested: Xvid, DivX, mpeg4, etc.)
- use menu File/Save As Avi... to encode and save the animation on disk.
Listing
In the following we report the entire source code for reference.
#include "chrono/assets/ChVisualShapeBox.h"
#include "chrono/assets/ChCamera.h"
#include "chrono/assets/ChVisualShapeCylinder.h"
#include "chrono/assets/ChVisualShapeModelFile.h"
#include "chrono/assets/ChVisualShapeSphere.h"
#include "chrono/assets/ChTexture.h"
#include "chrono/physics/ChParticleCloud.h"
#include "chrono/physics/ChSystemNSC.h"
#include "chrono/core/ChRandom.h"
#include "chrono_postprocess/ChPovRay.h"
#include "chrono_thirdparty/filesystem/path.h"
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
std::cout << "Copyright (c) 2017 projectchrono.org\nChrono version: " << CHRONO_VERSION << std::endl;
if (!filesystem::create_directory(filesystem::path(out_dir))) {
std::cout << "Error creating directory " << out_dir << std::endl;
return 1;
}
" \
light_source { \
<2, 10, -3> \
color rgb<1.2,1.2,1.2> \
area_light <4, 0, 0>, <0, 0, 4>, 8, 8 \
adaptive 1 \
jitter\
} \
object{ Grid(1,0.02, rgb<0.7,0.8,0.8>, rgbt<1,1,1,1>) rotate <0, 0, 90> } \
");
auto floor = chrono_types::make_shared<ChBody>();
floor->SetFixed(true);
auto floor_mat = chrono_types::make_shared<ChContactMaterialNSC>();
auto floor_shape = chrono_types::make_shared<ChCollisionShapeBox>(floor_mat, 20, 1, 20);
floor->EnableCollision(true);
auto boxfloor = chrono_types::make_shared<ChVisualShapeBox>(20, 1, 20);
boxfloor->SetColor(
ChColor(0.3f, 0.3f, 0.6f));
auto body = chrono_types::make_shared<ChBody>();
body->SetFixed(true);
auto sphere = chrono_types::make_shared<ChVisualShapeSphere>(0.5);
auto mbox = chrono_types::make_shared<ChVisualShapeBox>(0.4, 1.0, 0.2);
auto cyl = chrono_types::make_shared<ChVisualShapeCylinder>(0.3, 0.7);
body->AddVisualShape(chrono_types::make_shared<ChVisualShapeSphere>(0.03),
body->AddVisualShape(chrono_types::make_shared<ChVisualShapeSphere>(0.03),
auto objmesh = chrono_types::make_shared<ChVisualShapeModelFile>();
for (int j = 0; j < 20; j++) {
auto smallbox = chrono_types::make_shared<ChVisualShapeBox>(0.2, 0.2, 0.02);
smallbox->SetColor(
ChColor(j * 0.05f, 1 - j * 0.05f, 0.0f));
body->AddVisualShape(smallbox,
ChFrame<>(pos, rot));
}
auto camera = chrono_types::make_shared<ChCamera>();
camera->SetAngle(50);
body->AddCamera(camera);
auto particles = chrono_types::make_shared<ChParticleCloud>();
auto particle_mat = chrono_types::make_shared<ChContactMaterialNSC>();
auto particle_shape = chrono_types::make_shared<ChCollisionShapeSphere>(particle_mat, 0.05);
particles->AddCollisionShape(particle_shape);
particles->EnableCollision(true);
for (int np = 0; np < 100; ++np)
auto sphereparticle = chrono_types::make_shared<ChVisualShapeSphere>(0.05);
particles->AddVisualShape(sphereparticle);
std::cout <<
"time= " << sys.
GetChTime() << std::endl;
}
return 0;
}



